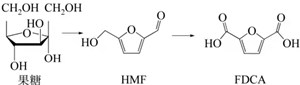
The preparation of FDCA furan dicarboxylic acid by the HMF route of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural has received great attention from scientific research and industry, and significant progress has been made. It is expected to be the first method to achieve industrial production.
The synthetic route of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural HMF using fructose as raw material can be traced back to 1977. From 2000 to 2002, Seri et al. compared the dehydration reactions of monosaccharides in water using lanthanide chlorides as catalysts and found that the yield of fructose to HMF was significantly higher than that of other monosaccharides such as glucose, mannose, and galactose. Therefore, fructose synthesized from monosaccharides such as glucose becomes the main raw material source for HMF production.
However, in the process of producing HMF from fructose, dehydration of fructose will inevitably produce small molecule acids such as formic acid, acetic acid, and acetic acid. Under the acid catalyzed system, various by-products such as soluble polymers and insoluble humus are generated, which affect the separation and purification of HMF. In theory, 1.43 tons of fructose can produce 1 ton of HMF; In fact, 1.8-4 tons of fructose produce 1 ton of HMF (industrially).
According to the separation and purification, the HMF route of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural is usually divided into one pot method and two pot method (traditional kettle production process). The two pot method first dehydrates sugars to obtain HMF, separates and purifies HMF, and then uses it for oxidation synthesis of FDCA furan dicarboxylic acid. The one pot method involves dehydrating sugars to obtain HMF, which is then directly oxidized without separation to obtain the target product FDCA. The entire reaction is carried out in the same reactor. The one pot method requires the dehydration of sugars to obtain HMF, which can be directly oxidized without separation to obtain the target product FDCA. Suitable catalyst and solvent systems need to be designed to adapt to the respective characteristics of the two-step reaction. Compared to the two pot method, the one pot method has a simpler reaction process, but it has drawbacks such as lower yield of the target product.
Domestic companies such as Tangneng Technology, Hefei Lifu, and foreign AVA Biochem often use a two pot method to synthesize FDCA furan dicarboxylic acid, while Avantium in the Netherlands uses a one pot method to synthesize FDCA.
In addition, the continuous production process of Zhongke Guosheng in China, which produces 5-hydroxymethylfurfural HMF and FDCA furan dicarboxylic acid from fructose, has attracted industry attention. Unlike traditional batch production in a kettle, the purity of FDCA reaches 99.9%, greatly improving the conversion rate of FDCA.
The advantage of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural HMF over other methods is that HMF can not only be used to produce FDCA furan dicarboxylic acid, but also copolymerize with diols and diamines to further manufacture polyester and nylon materials. In addition, fine chemicals are also the main market for HMF applications, which can be used to manufacture bio based water-based adhesives, bio based surfactants, bio based environmental protection coatings, bio based disinfection and sterilization products, bio based plasticizers, and bio based anti-corrosion materials.
Shandong Yino Biologic Materials is a furfural manufacturer that uses biobased materials as raw materials to produce furfuryl alcohol, furfural, tetrahydrofurfurfuryl alcohol, 2-methylfuran, 2-methyltetrahydrofuran, N-methylpyrrolidone, biobased pentanediol series products, etc. It has obvious advantages such as green and low-carbon, and raw material regeneration.
Content collected and organized from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for deletion